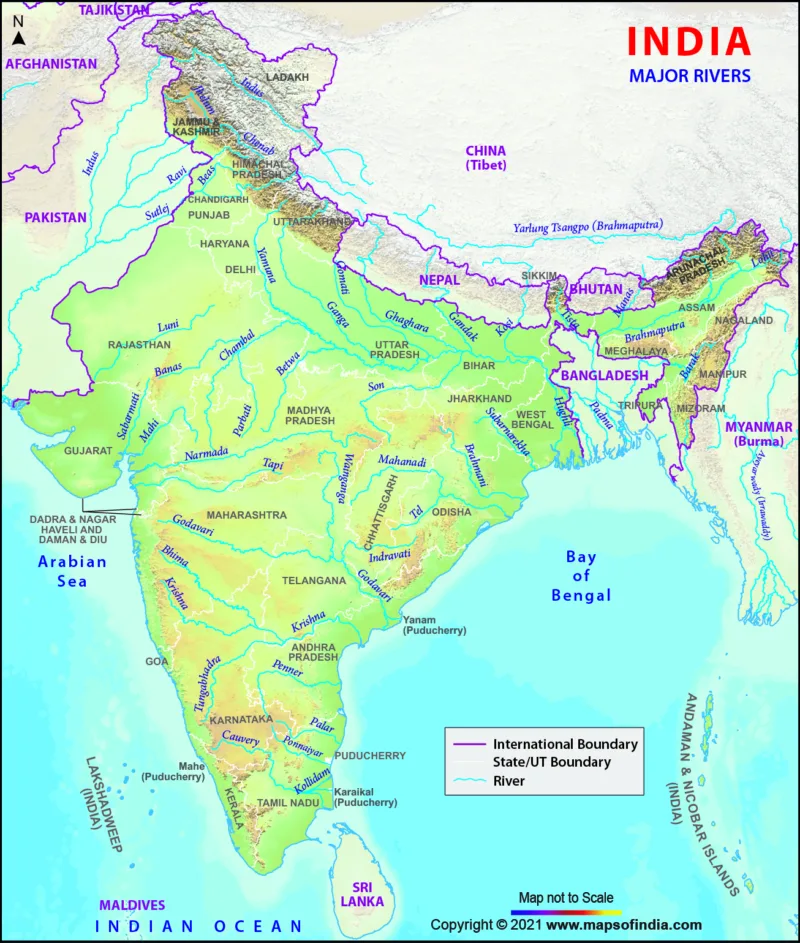
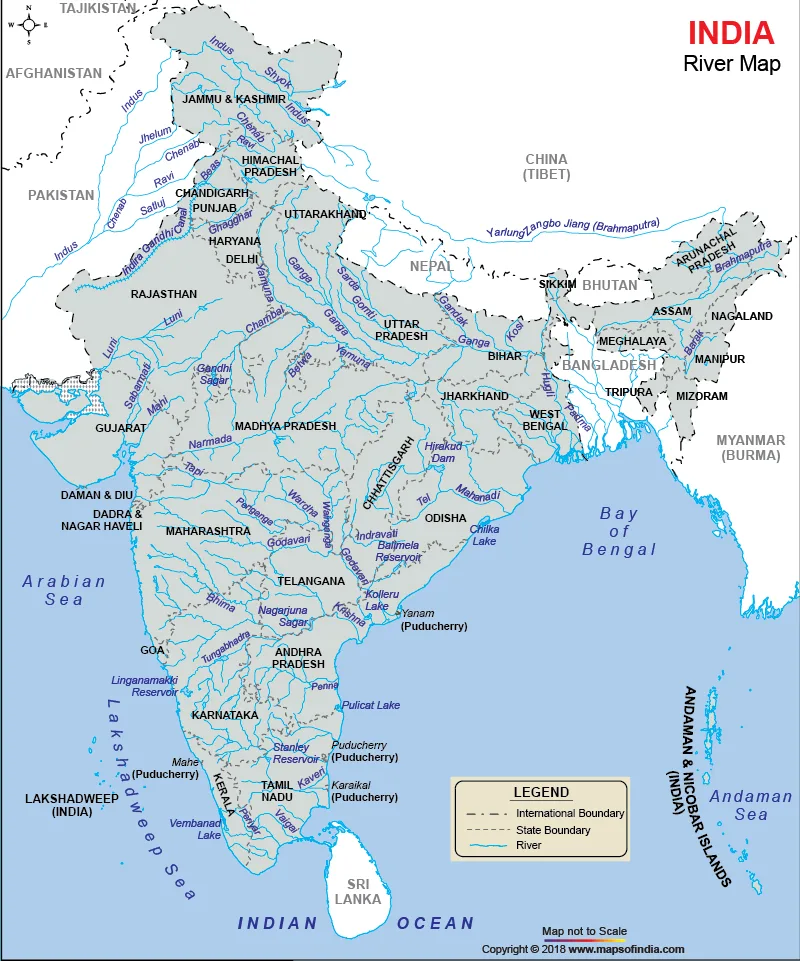
India’s River Map: In this article, we will delve into the intricate network of rivers that crisscross the vast landscape of India. India, known for its rich cultural diversity, is equally renowned for its diverse geography, and its rivers play a pivotal role in shaping the nation’s topography and culture. Join us on this journey as we navigate through the river map of India and uncover the stories, significance, and challenges associated with these lifelines of the nation.
Introduction to India’s River System
India boasts an extensive river system that can be broadly categorized into major river basins. These rivers are primarily fed by the melting snow from the Himalayas, making them a vital source of freshwater for the Indian subcontinent.
The Ganges River Basin
Our exploration begins with the holiest of all Indian rivers, the Ganges. Originating from the Gangotri Glacier in Uttarakhand, this mighty river flows through the northern plains and eventually merges with the Bay of Bengal. Discover the spiritual and cultural importance of the Ganges in Indian society.
The Brahmaputra River Basin
Heading east, we encounter the Brahmaputra River, which originates in Tibet and flows through northeastern India. Explore the unique features of this transboundary river, its impact on the region, and the challenges it poses.
Peninsular Rivers: A Diverse Landscape
Moving southwards, we enter the peninsular region of India, where a myriad of rivers traverse the Deccan Plateau, offering a stark contrast to the northern plains.
The Godavari River
The Godavari, often referred to as the “Dakshin Ganga,” is the second-longest river in India. Uncover its significance in providing irrigation and livelihood to millions in the southern states.
The Krishna River
Flowing parallel to the Godavari, the Krishna River has its own tales to tell. Learn about its historical importance and the role it plays in agriculture in the Deccan region.
The Cauvery River
The Cauvery River, known for its scenic beauty, serves as a lifeline for Karnataka and Tamil Nadu. Dive into the disputes and challenges surrounding its waters.
The Western Ghats and Coastal Rivers
As we approach the western coast of India, the Western Ghats give rise to several short but significant rivers.
The Narmada and Tapi Rivers
The Narmada and Tapi, flowing through the states of Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat, have a unique place in the geological history of India. Explore the stunning landscapes they carve through.
Himalayan Rivers: The Source of Life
Returning to the north, we revisit the Himalayan region, where some of India’s most iconic rivers originate.
The Yamuna River
The Yamuna, often overshadowed by the Ganges, has its own stories to narrate. Understand its importance in the Indian capital, Delhi, and the environmental challenges it faces.
Challenges and Conservation Efforts
Throughout our journey, we will shed light on the environmental challenges these rivers face, including pollution, encroachment, and changing weather patterns. Additionally, we will explore the various conservation efforts and initiatives aimed at preserving these invaluable water bodies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, India’s river map is not just a geographical phenomenon but a reflection of its cultural, historical, and ecological diversity. These rivers have shaped civilizations, provided sustenance, and continue to inspire awe. As we navigate through their waters, let us also recognize our responsibility to protect and preserve them for generations to come.
FAQs
1. Are the rivers of India only significant for their religious and cultural importance?
While religious and cultural significance is undeniable, these rivers also play a crucial role in agriculture, transportation, and ecology.
2. How polluted are India’s rivers, and what steps are being taken to combat this issue?
India’s rivers face varying degrees of pollution. Government initiatives and NGOs are actively working to reduce pollution and promote clean river systems.
3. Can I explore these rivers as a tourist, and are there any specific precautions to take?
Many of India’s rivers offer tourism opportunities. However, it’s essential to follow safety guidelines and respect local customs and the environment.
4. Are there any endangered species in these river ecosystems?
Yes, several species, including the Ganges River dolphin and various fish species, are endangered due to habitat degradation. Conservation efforts are ongoing to protect them.
5. How can I contribute to river conservation efforts in India?
You can support conservation organizations, participate in clean-up drives, and raise awareness about the importance of preserving India’s rivers.
In this article, we’ve embarked on a journey through the river map of India, unraveling the significance and challenges these water bodies face. As we conclude, let us remember that these rivers are not just geographical features but living entities that deserve our care and protection.
India’s River Map